Part 1 - Setup Node Machine
Required equipment:
- USB Drive for Ubuntu Server installation
- Node Machine
- Personal computer
Hardware
Minimum Requirements
These are the minimum hardware requirements for a node machine. Always check LUKSO's documentation for updates.
- OS: Linux or Mac
- CPU: 2 cores
- RAM: 16GB
- Storage: 100GB SSD (solid state is required)
For a future-proof setup, you may wish to choose a system with 4 cores, a 2.8GHz processor, 1TB of SSD storage, and 32GB of RAM.
Example Hardware
Mini PCs are designed for 24/7 use and low power consumption, making them ideal for running a LUKSO node. The Intel NUC mini PC line is a common choice within the community. Below are the specs and pricing of three different NUC models.
| Intel NUC 10 | Intel NUC 10 Performance Kit | |
|---|---|---|
| Processor | i5 4-core | i7 6-core |
| RAM | 16GB | 32GB |
| Storage | 512GB | 1TB |
| Price | $629 | $949 |
A backup system (or parts) is also something to consider. If your node is offline, you will incur slashing penalties roughly equal to the rewards you would have gained while being online. For example, if you average 1 LYX per day in rewards, you will lose 1 LYX per day if offline.
Step 1 - Install Ubuntu Server
This guide will follow the steps for Ubuntu 22.04 LTS Server or Desktop as our node operating system, and we will interact with the node remotely from a personal computer/laptop.
You have the option to install the desktop version of Ubuntu and operate the node like a desktop computer with a keyboard, mouse and monitor attached. However, there are a number of reason to choose a server installation for you node.
Using Server + remote SSH access from a personal computer instead of directly attaching a keyboard/monitor to your node has security and performance benefits and also adds convenience.
- Security - Most importantly, it is best security practice to run only the software needed to operate a node. To setup, troubleshoot, and maintain your node, you will rely on a web browser to follow guides and chat applications (like Discord) for community support. With remote access, you can use these application from your personal computer, and simply copy/paste commands into the SSH terminal.
When you choose a server installation, the temptation to use the node for other purposes is removed.
Performance - Ubuntu Desktop uses more system resources. Ubuntu Server makes more resources available to your node software.
Convenience - Your node should be wired to your network, not connected through WiFi. Remote access removes the need to keep a keyboard and monitor connect to you node and allows you to place your node hidden away near your router. Only two connections are needed, one to your router and one to an electrical outlet.
Also, with SSH already enabled, you can easily setup access to node your from remote locations by enabling a VPN server, allowing you to perform maintenance and troubleshooting from anywhere with an internet connection.
The steps in this guide only enable remote access from a computer on the same network. Remote access from a location out side of your network will require additional steps that are not covered in this guide
1.1 - Create a bootable USB stick
Requirments
- 4GB or larger USB flash drive
- A personal computer
Follow these steps to download the ISO file and image the USB flash drive:
- Visit the Ubuntu Server download page.
- Choose "Download Ubuntu Server [current version] LTS"
- Follow the guide on Ubuntu's website. Choose the appropriate guide below for your personal computer's operating system.
Windows guide (In the Windows guide, ignore the "Ubuntu ISO" requirement. You only need to download Rufus in this step.)
1.2 - Install the server
- Attach a monitor and keyboard to your node machine.
- Follow Ubuntu's official guide to install the operating system.danger
Use a strong password for your node machine
noteSome options will appear which are not documented in the Ubuntu guide. Leave the settings unchanged and choose done for these options.
- After step 14 is complete and the system reboots, you should see a login screen.
If the login prompt does not appear, press enter.
- Login with the username and password created during the installation. After a successful login, you should see a
$prompt.
- Update the server with these three commands. Type the command, then press
Enter.
Read the output when executing commands!! Make sure you see no warning or errors.
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade -y
Press enter when asked which services should be restarted.
sudo apt install -y
- Install SSH.
sudo apt-get install openssh-server
- Install the Nano text editor.
sudo apt-get install nano -y
- Install curl.
sudo apt install curl
- Install Git.
sudo apt install git
Step 2 - Configure Settings
These steps will need to be typed into your node terminal to prepare for remote access.
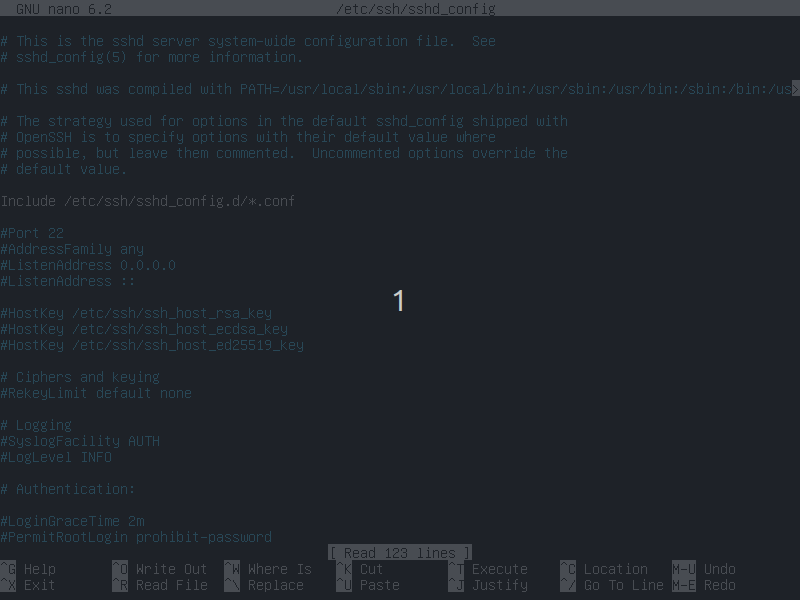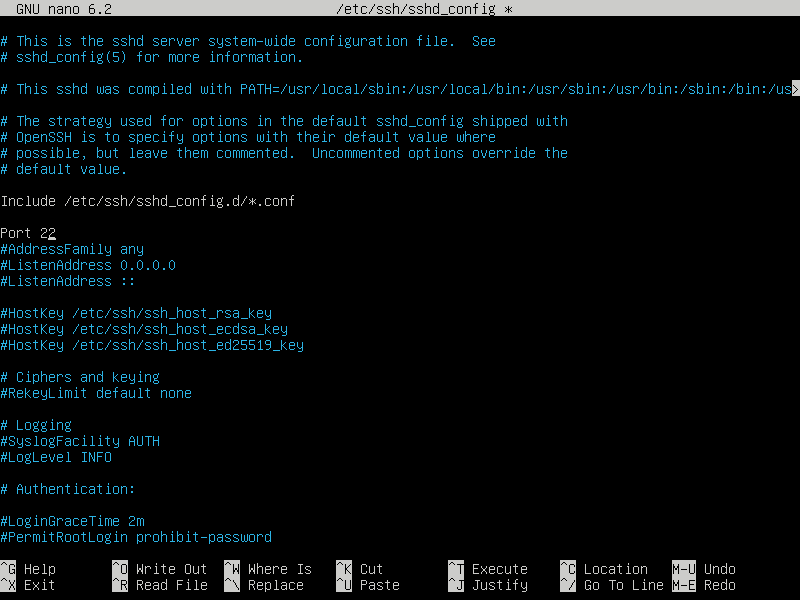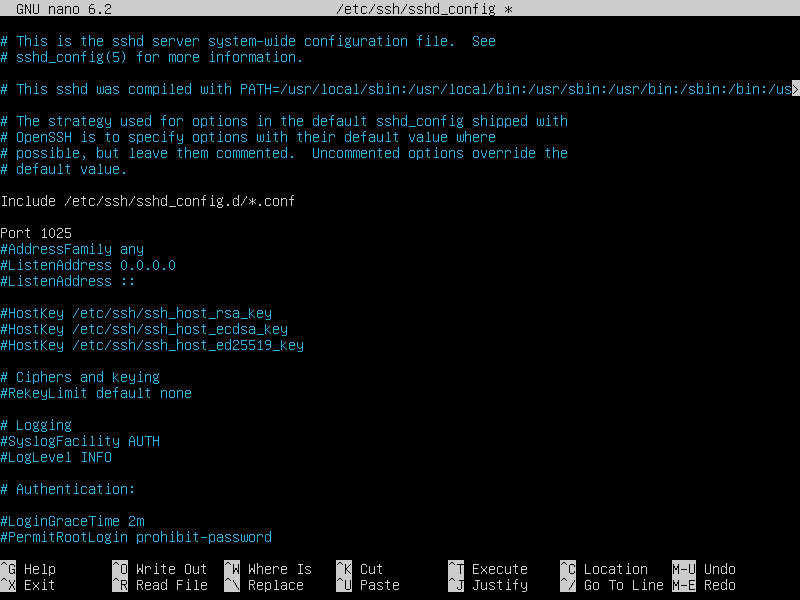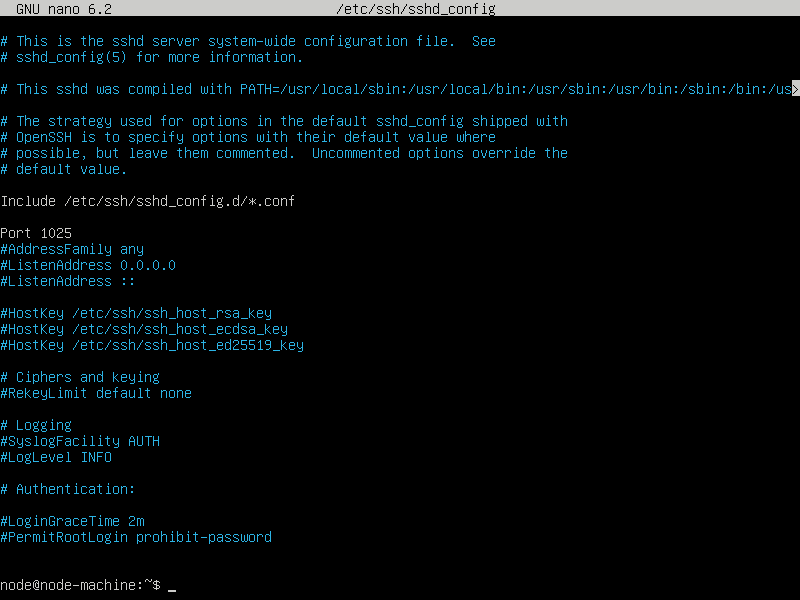
2.1 - Open the SSH config file
sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
2.2 - Change SSH Port Number
The default SSH port (22) should be changed to a random number for security reasons.
- Find
#Port 22 - Remove the
# - Choose a number between 1024 thru 49141
- Replace
22with your number - Close editor by pressing
ctrl+X, then save.
In this example, we are using port 1025
For the rest of this guide when you see <ssh-port> replace it with the number you chose in this step.
- Validate SSH configuration and restart ssh service.
sudo sshd -t
sudo systemctl restart sshd
2.3 - Configure firewall
1 - By default deny all traffic
sudo ufw default deny incoming
sudo ufw default allow outgoing
Verify the output of the commands
2 - Allow SSH access
For this command, replace <ssh-port> with the number you chose in step 2.2
sudo ufw allow <ssh-port>/tcp
Verify the output of the command
3 - Enable firewall
sudo ufw enable
Verify the output of the command
4 - Confirm firewall settings
sudo ufw status
Verify the output of the command
Step 3 - Configure Auto Start
It is important to set up your node to power on automatically after a power outage. The setting is usually found in the BIOS, but some systems use a jumper on the motherboard. Refer to your hardware manual for instructions.
3.1 - Shut down the node machine
sudo shutdown -h now
3.2 - Configure BIOS
To enter the BIOS, you must press a key on the keyboard just after the machine is powered on. It is often F2 but can vary from system to system.
For Intel NUC, follow these steps:
- Power on your node machine
- Press F2 before the server boots to enter BIOS setup
- Go to
Power->Secondary Power Settingsmenu - Set the option for
After Power FailuretoPower On - Press F10 to save changes and exit BIOS
- All you system to boot back to the login screen
3.3 - Test Settings
Test the setting by unplugging the power cord while the system is running. It should turn on and boot when you plug it back in.
Step 4 - Reserve Node IP Address
Address reservation ensures your router always assigns the same IP address to your node. This step will require logging into the settings screen of your router. The steps are different for each manufacturer.
For these step, you will need your node machine and personal computer.
4.1 - Log in to router
- Log in to your node machine
- Determine your router's IP address.
ip route show default
the IP address displayed after default via is the address of your router.
- On your personal computer, open a web browser and enter the router's IP address.
A username and password prompt will appear. Login to access the router administrative console. If you do not now your credentials, you will need to reset your router. Refer to your router's manual for instructions on accessing the console.
4.2 - Configure Router
- Determine the IP address of your node
hostname -I
Find the setting for reserving IP addresses. “DHCP Settings” or “DHCP Reservation” are common terms. Refer to your router’s manual for specific instructions.
Configure the router to reserve this address
Save the settings
References